Molecular Visualization by Color
Coloring is a powerful way to highlight components, properties, and features of molecular structures. With Copilot, you can easily apply these techniques, simplifying visualization and analysis.
Color by Name
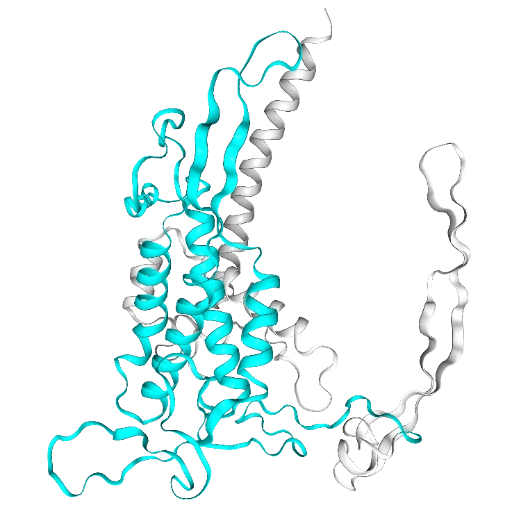
Color everything white. Then color residues 100-300 cyan.
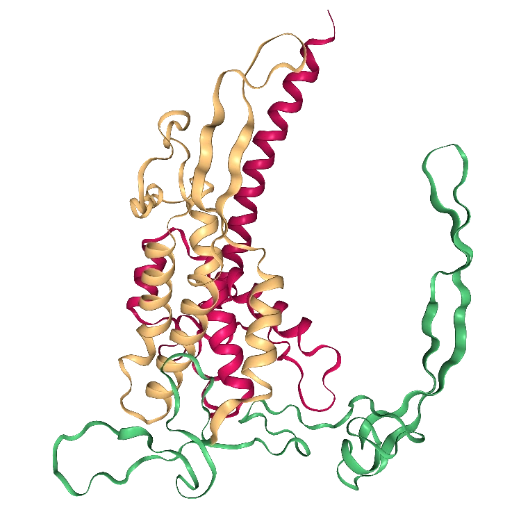
Color residues 1-120 ruby, residues 121-240 topaz, and residues 241-351 emerald
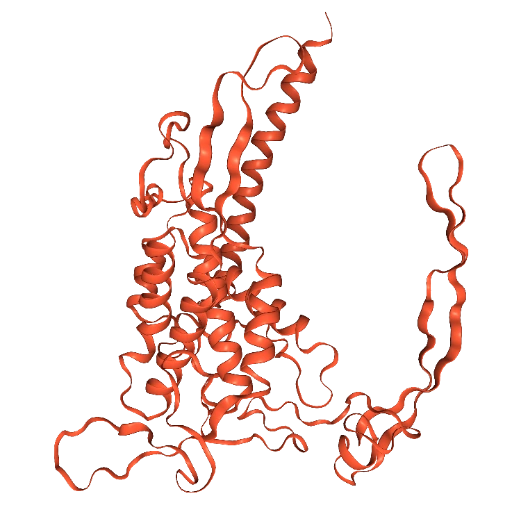
Color it #FF5733
Copilot recognizes standard color names like red, blue, or green as well as unusual names like peach, moonlight, or razmatazz, and hex codes for specific colors like #78FF00 or #0078FF.
Color Proteins by Their Secondary Structure
Color by secondary structure
This applies distinct colors to represent different secondary structures, namely helices, sheets, turns, and other.
Color Molecules by Their Atomic Chemical Elements
Show spheres and color by element
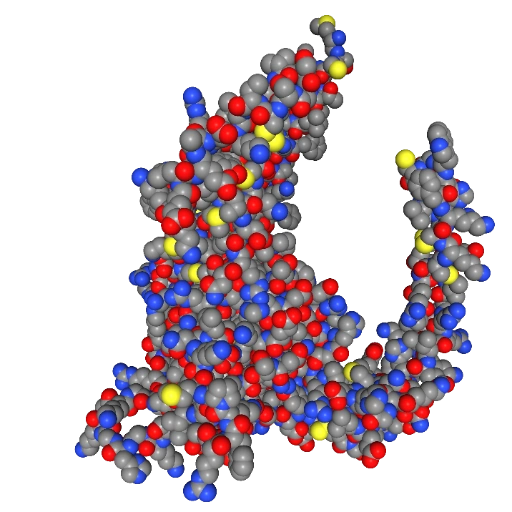

This method colors atoms according to standard conventions: C is gray, O is red, N is blue, H is white, and S is yellow, etc.
Color Molecules by Residue Name
Color by residue name
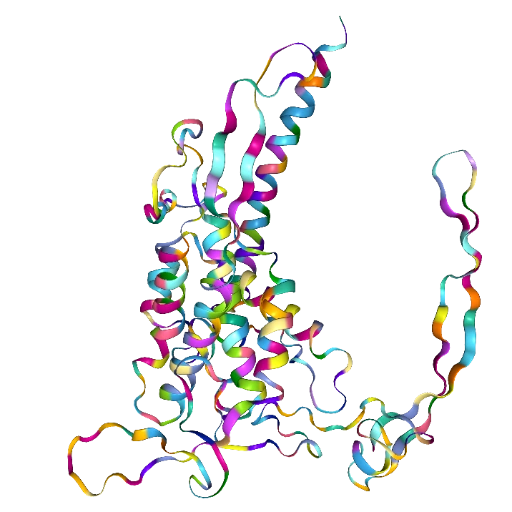
This method assigns a unique color to each residue name, allowing for easy differentiation between them.
Color Molecules by pLDDT Score
Color by plddt
This method uses a color scale to represent confidence levels: very low is orange, low is yellow, high is cyan, and very high is blue, assuming the b-factor column contains pLDDT values, which come from some, but not all, AI structure prediction algorithms.
Color Molecules by b-Factor Values
Color by b-factor
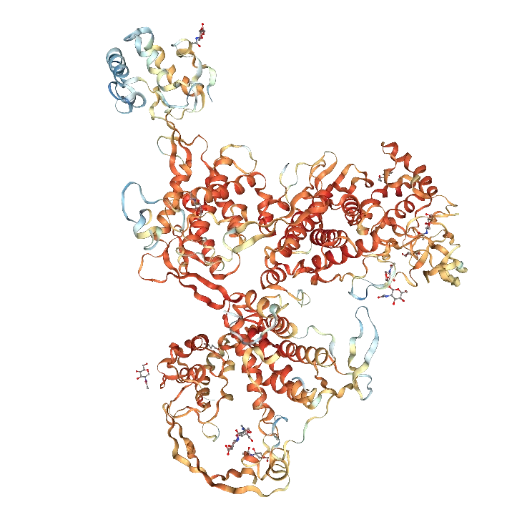
This technique applies a gradient based on the b-factor column to visualize variations in atomic displacement. This only applies to crystal structures.