DiffDock for Molecular Docking
DiffDock is a diffusion-based ML model for the docking of a protein to a small molecule. DiffDock reports a confidence score (-inf, inf) where a larger number is better, and scores below -1.5 can be considered low confidence. Note the confidence score does not predict the affinity, aka strength of the biochemical attraction, of the complex.
How to Use DiffDock
Dock asparagine into A0A1L9RXX7
Inputs
- PDB File
- Specifies the 3D structure of the target protein.
- SMILES String
- Specifies the identity of the small molecule or ligand.
Outputs
- PDB File
Specifies the predicted structure of the protein and the small molecule docked together.
- Confidence Score
A model confidence score (-inf, inf), where a larger number is better, and scores below -1.5 can be considered low confidence. Note the confidence score does not predict the affinity, aka strength of the biochemical attraction, of the complex.
Examples
Load the protein structure for uniprot ID P08100, load small molecule retinal, dock all-trans-Retinal into P08100
Dock biotin into P22629
Dock CC(C)CCCCC(=O)C1C(CO)COC1=O into C0STK5
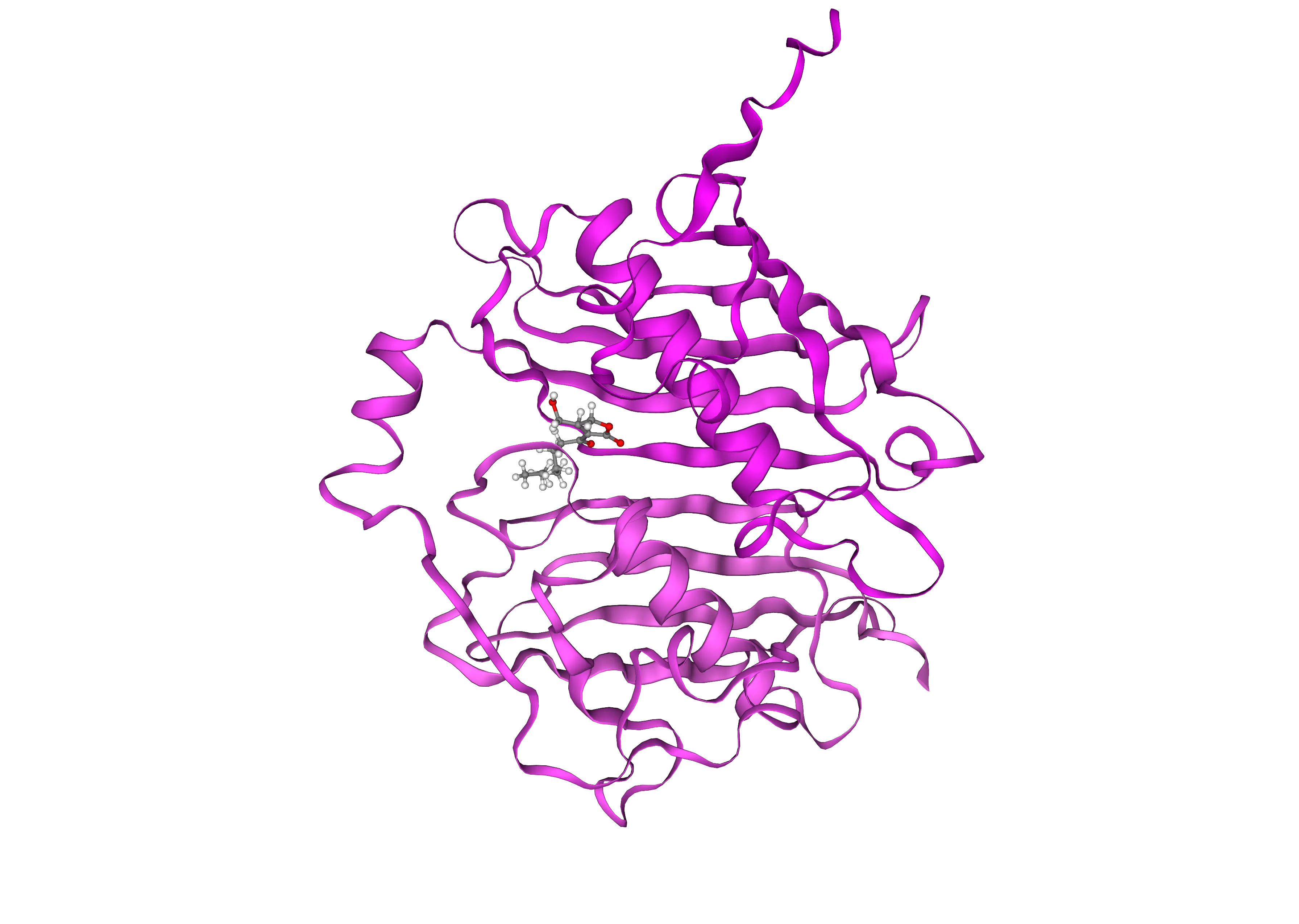
Analyzing Diffdock Results
Effective computational evaluation of docking results is essential for advancing drug discovery and molecular modeling, yet it remains an underdeveloped area.
Docking Results vs. Experimental Data: Aligning the docked structure with experimental data and calculating the root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) is the gold standard for validation, though experimental data is often unavailable.
Visual Inspection: Using molecular visualization tools, researchers can qualitatively assess docking results. It’s important to check for strong bonding patterns and shape complementarity at the binding interface and ensure that key residues, identified through mutational scanning, are involved in the interaction.