MP3 for Molecule Programming
MP3 is a transformer-based AI model for molecule programming that can be used for redesign, diversification, or de novo (from scratch) design of protein sequences.
How to use MP3 for Protein Design
Redesign A0A1L9RXX7 residues 40-60
Inputs
- Amino Acid Sequence
A single-chain protein sequence with a length of fewer than 300 amino acids.
- Function Description (optional)
A keyword describing the desired protein function, such as “leucine rich repeat” or “hydrolase.”
- Temperature (optional)
A parameter that influences the design; lower values introduce fewer changes, while higher values introduce more changes.
Outputs
- Designed Protein Sequence
The optimized amino acid sequence generated based on the input parameters.
Examples of MP3
Diversify Q7L266 with temperature 2.0
Redesign A0A328N043 with temperature 1.5 for the following ranges: residues 0-110 and residues 150-283
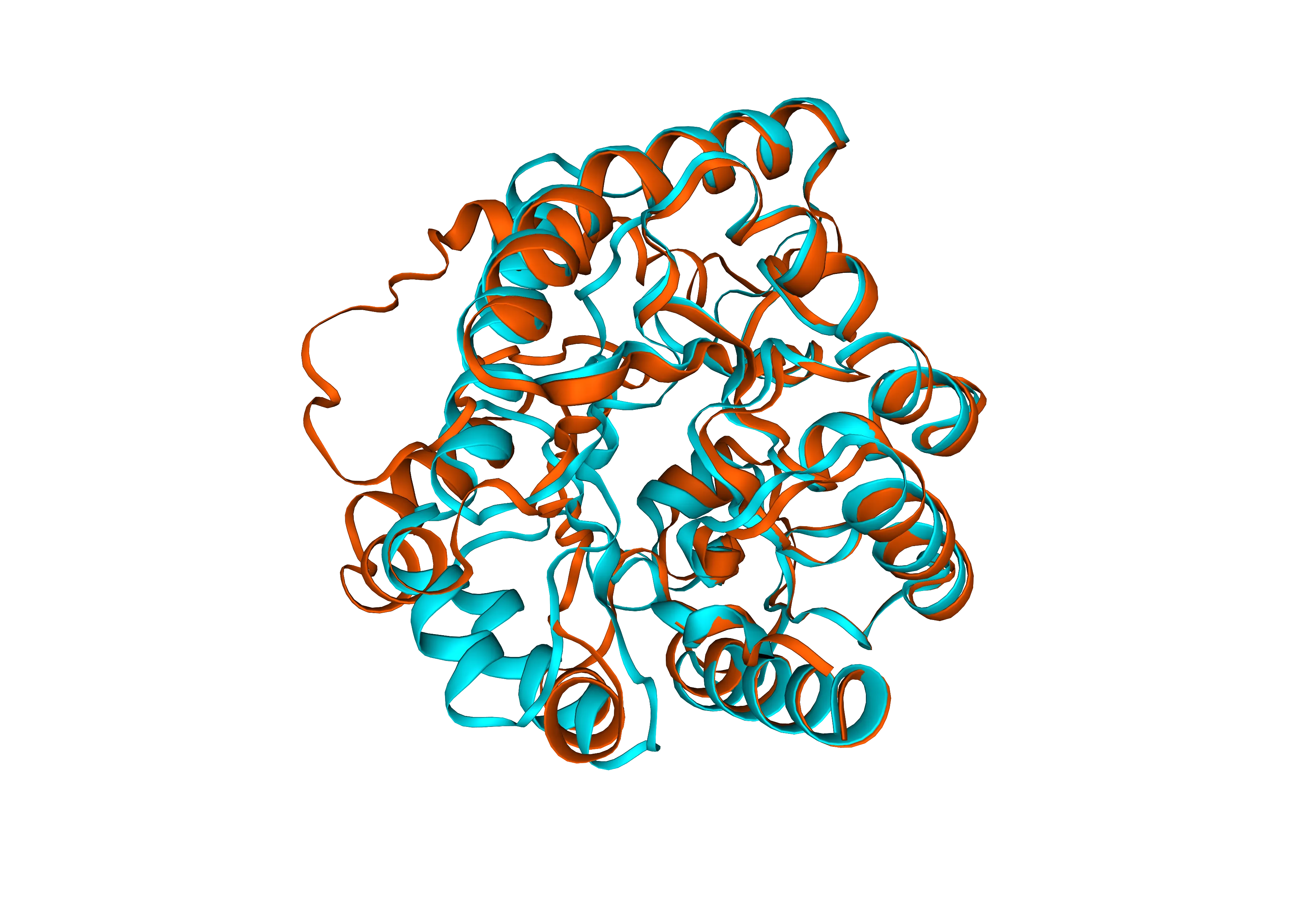
Create a de novo hydrolase
Create an asparagine protein